Bovine Tuberculosis Vaccine
Applying the CIT reduced these rates to only 058 in the VH and to 025 in the TC ons. Therefore a replacement or supplement to BCG is required.

New Vaccine Could Immunize 50 Million Cattle Against Bovine Tuberculosis Genetic Literacy Project
Bovis has led to renewed interest in the use of vaccines for the control of bovine tuberculosis TB.

Bovine tuberculosis vaccine
. Recent experimental trials with cattle have demonstrated that. But such a vaccination is currently illegal in Europe because vaccinated animals may test positive for infection creating confusion. Tuberculosis TB remains one of the most important infectious diseases of humans and animals. A new role for bacillus Calmette-Guérin BCG a vaccine originally developed for human TB has been shown to protect cattle against bovine TB BCG was originally developed by French scientists.Bacille Calmette-Guerin BCG is the worlds most widely used vaccine but there are concerns that it provides little protection against pulmonary tuberculosis of humans in countries that have a high prevalence of environmental mycobacteria. This article focuses on recent progress in animal TB vaccinology outlining that oral-route vaccination. Cattle that are vaccinated with the BCG vaccine which contains a harmless strain of the bovine TB pathogen Mycobacterium bovis produce a positive PPD test for TB making it impossible to. Experiments in cattle provide a model to investigate this situation and to develop an improved tuberculosis vaccine.
It is used mostly in the developing. The emergence of wildlife reservoirs of Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle as well as increased inter-regional trade with associated spread of M. World-leading bovine tuberculosis bTB TB cattle vaccination trials are set to get underway in England and Wales as a result of a major breakthrough by government scientists. The emergence of wildlife reservoirs of Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle as well as increased inter-regional trade with associated spread of M.
The only vaccine currently available for human and bovine TB is the live attenuated Bacille Calmette Guerin BCG. Mycobacterium bovisBCG the only currently available TB vaccine demonstrates variable levels of efficacy. Bovine tuberculosis remains a major economic and animal welfare concern worldwide. 1 subunit vaccines.
Bovine TB is an infectious disease in cattle affecting their lungs and those that test positive for the disease are culled. This approach used alongside. In this article the authors discuss potential strategies by which Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccination may be improved to allow highly efficacious vaccination of cattle. Field efficacy trials performed in the early 20th century demonstrated the partial effectiveness of bacilli Calmette-Guerin BCG for the control of bovine TB.
However protection against TB conferred by BCG is variable and to this date the reasons for the successes and failures of BCG. Previous work with small-animal laboratory models of tuberculosis has shown that vaccination strategies based on heterologous prime-boost protocols using Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin BCG to prime and modified vaccinia virus Ankara strain MVA85A or recombinant attenuated adenoviruses Ad85A expressing the mycobacterial antigen Ag85A to boost may increase the protective efficacy of BCG. Bovis has led to renewed interest in the use of vaccines for the control of bovine tuberculosis TB. The emergence of wildlife reservoirs of Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle as well as increased inter-regional trade with associated spread of M.
These strategies are also highly applicable to the fight against tuberculosis in humans. Developing a vaccine that would protect cattle against bovine tuberculosis is a potential alternative approach being investigated by the UK government. BCG is thought to confer protection through the induction of Th1 responses against mycobacteria. Vaccination of cattle in combination with more specific and sensitive diagnostic tests is suggested as the most effective strategy for bovine TB control.
This approach used alongside conventional control policies also requires the development of vaccine-compatible diagnostic assays to distinguish vaccinated from infected animals DIVA. Pre-vaccination positive results rate was 240 among the 7 herds in the single bovine intradermal tuberculin test BSIT. Field efficacy trials performed in the early 20th century demonstrated the partial effectiveness of bacilli Calmette-Guerin BCG for the control of bovine TB. The BCG vaccine which is currently used to protect humans against TB.
The only vaccine currently available for human and bovine tuberculosis is Bacillus Calmette-Guérin which is known to have variable efficacy for both species. Developing the vaccine In the 1910s Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin developed a way of culturing the bovine tuberculosis bacillus Mycobacterium bovis that made it less virulent. The use of a bacillus Calmette-Guerin BCG-based vaccine could represent a viable strategy for controlling bovine tuberculosis TB principally in those cases where a wildlife disease vector exists. Two years later it rose to 2042 in the VH and remained below at 075 in the TC.
The BVDP study area. Cattle vaccination is being considered as part of control strategies. The BCG vaccine was developed for control of human tuberculosis by Albert Calmette and Camille Guerin by repeated sub-culturing of the bovine TB bacillus Mycobacterium bovis until it lost. The Badger Vaccine Deployment Project BVDP was initiated in July 2009.
The project was intended to provide the first use of a vaccine for bovine tuberculosis bTB in badgers outside of research trials and to offer information on the practicalities of the dissemination of badger vaccination. The BCG vaccine that is used to protect humans against tuberculosis contains an attenuated or weakened strain of the tubercle bacillus Mycobacterium bovis. We discuss progress made on optimizing the only potentially available vaccine bacille Calmette Guérin BCG and on strategies to improve BCG. In the third of a series of BCG vaccination trials calves.

Bcg Compatible Diva Skin Tests For Cattle Vaccinated Against Bovine Tuberculosis Oie Bulletin

Bcg Compatible Diva Skin Tests For Cattle Vaccinated Against Bovine Tuberculosis Oie Bulletin
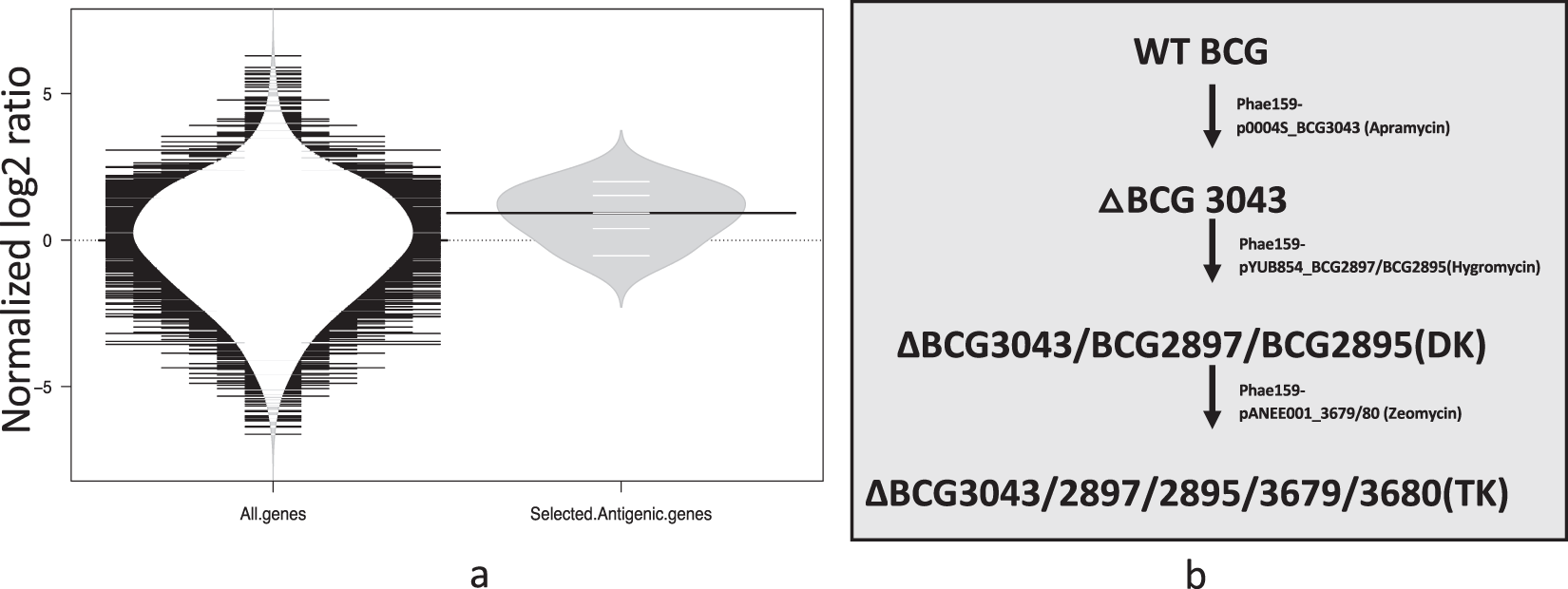
Development Of A Diagnostic Compatible Bcg Vaccine Against Bovine Tuberculosis Scientific Reports

Use Of Bcg Vaccination For Bovine Tuberculosis Control Oie Bulletin

No Silver Bullet Cattle Vaccine To Beat Bovine Tb Farmers Weekly
Study Highlights Scale Of Field Trials For Bovine Tb Vaccine Animal Health Media
It is used mostly in the developing. This approach used alongside.

No Silver Bullet Cattle Vaccine To Beat Bovine Tb Farmers Weekly
Cattle that are vaccinated with the BCG vaccine which contains a harmless strain of the bovine TB pathogen Mycobacterium bovis produce a positive PPD test for TB making it impossible to.

Bovine tuberculosis vaccine
. Bovine tuberculosis remains a major economic and animal welfare concern worldwide. These strategies are also highly applicable to the fight against tuberculosis in humans. Tuberculosis TB remains one of the most important infectious diseases of humans and animals. However protection against TB conferred by BCG is variable and to this date the reasons for the successes and failures of BCG.Experiments in cattle provide a model to investigate this situation and to develop an improved tuberculosis vaccine. Cattle vaccination is being considered as part of control strategies. The emergence of wildlife reservoirs of Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle as well as increased inter-regional trade with associated spread of M. The BCG vaccine which is currently used to protect humans against TB.
The BVDP study area. In this article the authors discuss potential strategies by which Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccination may be improved to allow highly efficacious vaccination of cattle. We discuss progress made on optimizing the only potentially available vaccine bacille Calmette Guérin BCG and on strategies to improve BCG. The emergence of wildlife reservoirs of Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle as well as increased inter-regional trade with associated spread of M.
A new role for bacillus Calmette-Guérin BCG a vaccine originally developed for human TB has been shown to protect cattle against bovine TB BCG was originally developed by French scientists. World-leading bovine tuberculosis bTB TB cattle vaccination trials are set to get underway in England and Wales as a result of a major breakthrough by government scientists. The BCG vaccine that is used to protect humans against tuberculosis contains an attenuated or weakened strain of the tubercle bacillus Mycobacterium bovis. In the third of a series of BCG vaccination trials calves.
The BCG vaccine was developed for control of human tuberculosis by Albert Calmette and Camille Guerin by repeated sub-culturing of the bovine TB bacillus Mycobacterium bovis until it lost. 1 subunit vaccines. Bovine TB is an infectious disease in cattle affecting their lungs and those that test positive for the disease are culled. Recent experimental trials with cattle have demonstrated that.
Bacille Calmette-Guerin BCG is the worlds most widely used vaccine but there are concerns that it provides little protection against pulmonary tuberculosis of humans in countries that have a high prevalence of environmental mycobacteria. Field efficacy trials performed in the early 20th century demonstrated the partial effectiveness of bacilli Calmette-Guerin BCG for the control of bovine TB. Developing the vaccine In the 1910s Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin developed a way of culturing the bovine tuberculosis bacillus Mycobacterium bovis that made it less virulent. Field efficacy trials performed in the early 20th century demonstrated the partial effectiveness of bacilli Calmette-Guerin BCG for the control of bovine TB.
The emergence of wildlife reservoirs of Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle as well as increased inter-regional trade with associated spread of M. Two years later it rose to 2042 in the VH and remained below at 075 in the TC. Vaccination of cattle in combination with more specific and sensitive diagnostic tests is suggested as the most effective strategy for bovine TB control. The Badger Vaccine Deployment Project BVDP was initiated in July 2009.
Pre-vaccination positive results rate was 240 among the 7 herds in the single bovine intradermal tuberculin test BSIT. The only vaccine currently available for human and bovine tuberculosis is Bacillus Calmette-Guérin which is known to have variable efficacy for both species. Previous work with small-animal laboratory models of tuberculosis has shown that vaccination strategies based on heterologous prime-boost protocols using Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin BCG to prime and modified vaccinia virus Ankara strain MVA85A or recombinant attenuated adenoviruses Ad85A expressing the mycobacterial antigen Ag85A to boost may increase the protective efficacy of BCG. But such a vaccination is currently illegal in Europe because vaccinated animals may test positive for infection creating confusion.
The project was intended to provide the first use of a vaccine for bovine tuberculosis bTB in badgers outside of research trials and to offer information on the practicalities of the dissemination of badger vaccination. BCG is thought to confer protection through the induction of Th1 responses against mycobacteria. Developing a vaccine that would protect cattle against bovine tuberculosis is a potential alternative approach being investigated by the UK government. The use of a bacillus Calmette-Guerin BCG-based vaccine could represent a viable strategy for controlling bovine tuberculosis TB principally in those cases where a wildlife disease vector exists.
The only vaccine currently available for human and bovine TB is the live attenuated Bacille Calmette Guerin BCG. Bovis has led to renewed interest in the use of vaccines for the control of bovine tuberculosis TB. Mycobacterium bovisBCG the only currently available TB vaccine demonstrates variable levels of efficacy. This article focuses on recent progress in animal TB vaccinology outlining that oral-route vaccination.
This approach used alongside conventional control policies also requires the development of vaccine-compatible diagnostic assays to distinguish vaccinated from infected animals DIVA.
Study Highlights Scale Of Field Trials For Bovine Tb Vaccine Animal Health Media

Development Of A Diagnostic Compatible Bcg Vaccine Against Bovine Tuberculosis Scientific Reports

New Vaccine Could Immunize 50 Million Cattle Against Bovine Tuberculosis Genetic Literacy Project

Use Of Bcg Vaccination For Bovine Tuberculosis Control Oie Bulletin

Bcg Compatible Diva Skin Tests For Cattle Vaccinated Against Bovine Tuberculosis Oie Bulletin

Bcg Compatible Diva Skin Tests For Cattle Vaccinated Against Bovine Tuberculosis Oie Bulletin
Post a Comment for "Bovine Tuberculosis Vaccine"